Animal Nutrition and Physiology
In our previous VKE grant project, we comprehensively investigated the effect of omega-3 fatty acids on smooth muscle contractions. Recent research in rats has shown that fish oil rich in n-3 PUFA has a strain-dependent effect on sex hormone status and uterine contractions in rats. The response to PUFA intake can vary significantly within a given species, which may have implications for both animal nutrition and human nutrition. Our joint publication presenting the research conducted by the colleagues of the University of Szeged was published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences.
Omega-3 Fatty Acid Consumption Alters Uterine Contraction: A Comparative Study on Different Breeds of Rats
Kalman F. Szucs, Dora Vigh, Seyedmohsen Mirdamadi, Reza Samavati, Annamaria Schaffer, Tamara Barna, Tamás Tóth, György Bázár, Henrik Baranyay, Robert Gaspar
Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) play roles in several physiological and pathophysiological processes, but their effects on reproductive function are controversial. The aim of the study was to investigate the effect of n-3 PUFA-rich fish oil and n-6-rich sunflower oil on sex hormone status, in vivo and in vitro uterine contractility, and endometrial remodeling. Female Sprague Dawley, Lister hooded, and Wistar rats were treated orally for 20 days with 1 mL of tap water, sunflower oil, or fish oil. Blood samples were taken for gonadotropic and sex hormone analysis. In vivo smooth muscle contractions were measured weekly by electromyography. Isolated uterine and cecal contractions were measured after sacrificing the animals. Endometrial remodeling was detected based on the presence of αvβ3 integrin by optical imaging. In Sprague Dawley rats, fish oil increased the LH level and progesterone/estradiol (P4/E2) ratio compared to the sunflower oil-treated group. Uterine contractions were reduced both in vitro and in vivo. Endometrial αvβ3 integrin activity was increased in the fish oil group. In Lister hooded rats, neither sunflower nor fish oil treatments modified the investigated parameters. However, in Wistar rats, both oils increased only the in vivo contractions and reduced the P4/E2 ratio, along with αvβ3 integrin fluorescence. n-3 PUFA-rich fish oil induces a breed-dependent effect on sex hormone status and uterine contractions in rats. The response to PUFA intake may vary significantly within a given species, which may have importance both in animal feeding and human nutrition.
Access the full paper free of charge on the website of the journal:
» Omega-3 Fatty Acid Consumption Alters Uterine Contraction: A Comparative Study on Different Breeds of Rats
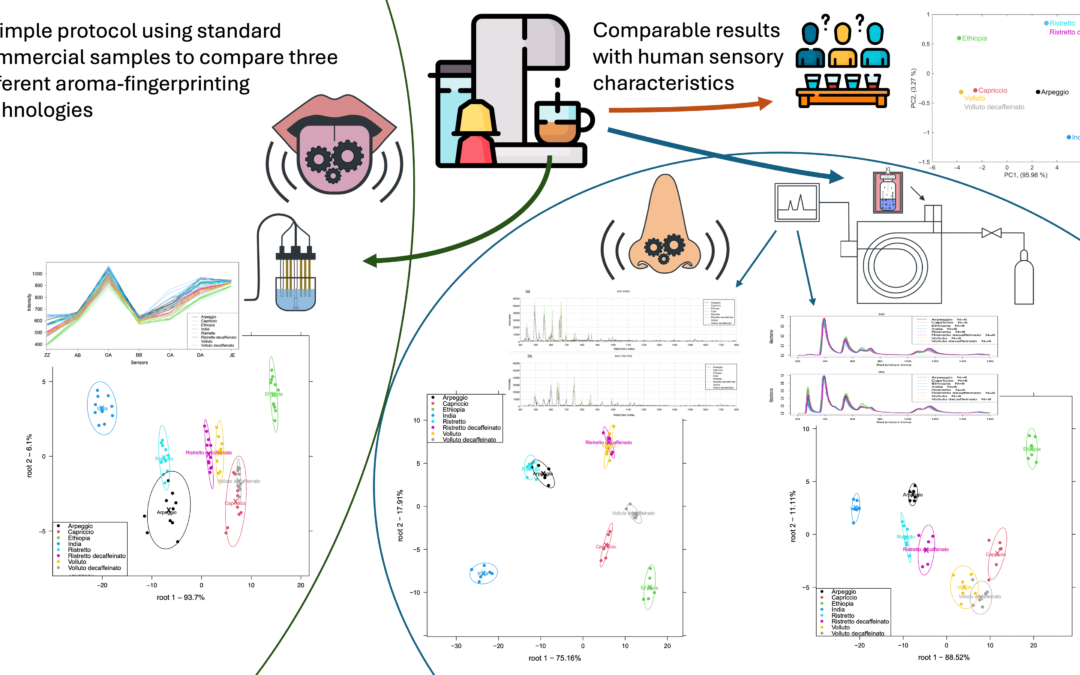
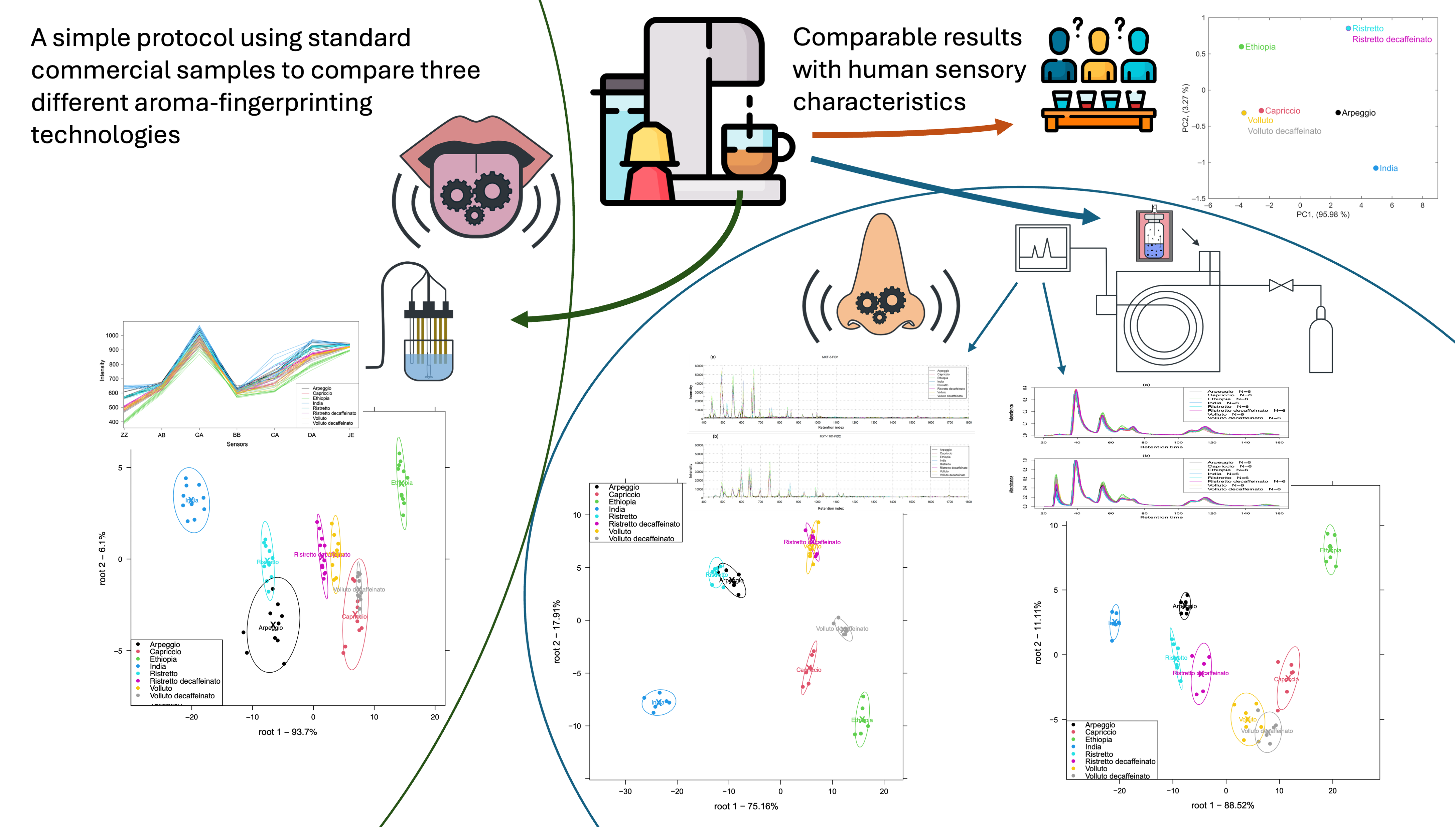
Instrumental Aroma Analysis
It is often difficult to compare two or more devices, either during development or purchase, especially when they are operating in different parts of the world during testing. Based on the examination of coffee capsules of consistent quality, which are easily available worldwide, we have developed a methodology with which instrumental aroma testing technologies operating on different principles can be quickly compared, regardless of whether they operate in the world. Our article published in the journal Chemosensors presents the results of three significantly different devices. The surprisingly similar results show a good correlation with the results of human sensory properties. The method is suitable for comparing newly developed technologies with previous, already proven technologies; assessing their reliability, and determining which technologies provide results that are more closely related to human sensory properties; and which technologies reinforce or complement each other depending on whether they provide identical or different results when examining the same set of samples.
Coffees Brewed from Standard Capsules Help to Compare Different Aroma Fingerprinting Technologies—A Comparison of an Electronic Tongue and Electronic Noses
Biborka Gillay, Zoltan Gillay, Zoltan Kovacs, Viktoria Eles, Tamas Toth, Haruna Gado Yakubu, Iyas Aldib, George Bazar
With the development of various new types of instrumental aroma sensing technologies, there is a need for methodologies that help developers and users evaluate the performance of the different devices. This study introduces a simple method that uses standard coffee beverages, reproducible worldwide, thus allowing users to compare aroma sensing devices and technologies globally. Eight different variations of commercial coffee capsules were used to brew espresso coffees (40 mL), consisting of either Arabica coffee or a blend of Robusta and Arabica coffee, covering a wide range of sensory attributes. The AlphaMOS Astree electronic tongue (equipped with sensors based on chemically modified field-effect transistor technology) and the AlphaMOS Heracles NEO and the Volatile Scout3 electronic noses (both using separation technology based on gas chromatography) were used to describe the taste and odor profiles of the freshly brewed coffee samples and also to compare them to the various sensory characteristics declared on the original packaging, such as intensity, roasting, acidity, bitterness, and body. Linear discriminant analysis (LDA) results showed that these technologies were able to classify the samples similarly to the pattern of the coffees based on the human sensory characteristics. In general, the arrangement of the different coffee types in the LDA results—i.e., the similarities and dissimilarities in the types based on their taste or smell—was the same in the case of the Astree electronic tongue and the Heracles electronic nose, while slightly different arrangements were found for the Scout3 electronic nose. The results of the Astree electronic tongue and those of the Heracles electronic nose showed the taste and smell profiles of the decaffeinated coffees to be different from their caffeinated counterparts. The Heracles and Scout3 electronic noses provided high accuracies in classifying the samples based on their odor into the sensory classes presented on the coffee capsules’ packaging. Despite the technological differences in the investigated devices, the introduced coffee test could assess the similarities in the taste and odor profiling capacities of the aroma fingerprinting technologies. Since the coffee capsules used for the test can be purchased all over the world in the same quality, these coffees can be used as global standard samples during the comparison of different devices applying different measurement technologies. The test can be used to evaluate instrumentational and data analytical developments worldwide and to assess the potential of novel, cost-effective, accurate, and rapid solutions for quality assessments in the food and beverage industry.
Access the full paper free of charge on the website of the journal:
» Coffees Brewed from Standard Capsules Help to Compare Different Aroma Fingerprinting Technologies—A Comparison of an Electronic Tongue and Electronic Noses
Instrumental Aroma Analysis, Near-infrared Spectroscopy
A new book titled “Sustainable Animal Agriculture – Global Challenges and Practical Solutions” is being published by the London-based publisher IntechOpen. In response to the honorable request, our colleagues contributed to the book by preparing a chapter on green agricultural technologies and sustainable analytical methods, presenting the latest trends. The book chapter, published in the summer of 2025, can be downloaded for free from the publisher’s website.
Applications of Green Agricultural Technologies (GAT) and Sustainable Analytical Methods (SAM) in Precision Animal Agriculture and Product Quality Testing
Haruna Gado Yakubu, George Bazar and Tamas Toth
Modern agricultural development is primarily based on applying environmentally friendly and efficient technologies to deliver farm productivity. This chapter examines the advancements made in green agricultural technologies (GAT) and sustainable analytical methods (SAM) for precision animal production systems. The application of Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) enables real-time monitoring of pasture fields, animal behaviour and health. The application of NIR in the dairy industry has revolutionised feed and milk quality analyses, by providing real-time, accurate and precise nutritive and quality feedback. Smart feeding and milking have ensured efficient feeding and milking of a large number of animals within short periods. These technologies have significantly improved the efficiency of livestock production systems, enhanced ecosystem integrity, reduced drudgery, improved animal welfare and physiological conditions, and increased farmer income. Notwithstanding, the complexities involved in the application of some of the technologies and the high cost of almost all of them are hindering their adoption in low-income countries. Stakeholders and policymakers must collaborate effectively to make these technologies affordable in low-income countries, thereby enhancing precision livestock agriculture worldwide. On the other hand, where GAT and SAM are available, many expect a self-evident agricultural revolution simply to be an investment. Professionals, however, must understand that all new technologies and methods also require knowledge and experience in application, not only in development. Currently, most of the portable technologies are operational in offline mode, while others require network connectivity (online) for efficient operation. Manufacturers and users must consistently review the performance of these technologies for the effective design and development of future generations of the devices.
Access the full chapter free of charge on the website of the publisher:
» Applications of Green Agricultural Technologies (GAT) and Sustainable Analytical Methods (SAM) in Precision Animal Agriculture and Product Quality Testing
Animal Nutrition and Physiology
We conducted research together with colleagues from MATE, Hungarian University of Agriculture and Life Sciences, in which we investigated the effect of plant feed ingredients containing carvacrol and limonene on the production indicators and parasitological status of sheep in a Hungarian dairy herd. The scientific publication summarizing the results of the research was published in the open-access journal Veterinary Sciences.
Evaluation of a Phytogenic Feed Supplement Containing Carvacrol and Limonene on Sheep Performance and Parasitological Status on a Hungarian Milking Sheep Farm
Éva Varga-Visi, Gábor Nagy, Ágnes Csivincsik, Tamás Tóth
There is currently worldwide interest in phytogenic feed supplements (PFSs) because they can lead to improved animal production. The scope of the present study was to observe the impact of a feed supplement containing carvacrol (CAR) and limonene (LIM) on the performance and parasitological status of sheep. The feed supplement decreased the plasma levels of β-hydroxybutyrate (p < 0.001), triglycerides (p = 0.014), nonesterified fatty acids (p = 0.021), and fructosamine (p = 0.002) in lactating ewes after 42 days of supplementation, while the average live weight (p = 0.002) and average daily weight gain (p = 0.001) of their twin suckling lambs increased significantly by the end of the study. In another experiment, fattening lambs fed the same supplement showed a decrease in fecal egg number of gastrointestinal nematodes (p = 0.02) but no differences in live weight, average daily gain, or mean number of Haemonchus contortus nematodes in the abomasum. The results highlighted that the inclusion of carvacrol and limonene in the feed of lactating ewes effectively increased the weight gain of the suckling lambs, presumably due to the ewes’ improved energy, but further studies are needed to elucidate the effects of carvacrol and limonene against gastrointestinal parasites.
Access the full paper free of charge on the website of the journal:
» Evaluation of a Phytogenic Feed Supplement Containing Carvacrol and Limonene on Sheep Performance and Parasitological Status on a Hungarian Milking Sheep Farm

Instrumental Aroma Analysis, Near-infrared Spectroscopy
What has a greater impact on the quality of yogurt? The composition of raw milk or the yogurt culture used? In our scientific paper prepared with colleagues from MATE, Hungarian University of Agriculture and Life Sciences, and published in the journal Food Control, we sought answers to these questions.
Uncovering key factors in differentiating fermented milk by feeding type and probiotic potential with E-nose and NIRS techniques
Mariem Majadi, Omeralfaroug Ali, András Szabó, Tamás Tóth, George Bazar, Zoltan Kovacs
This study evaluates the capabilities of near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) and electronic nose (E-nose) in characterizing fermented milk, focusing on the impact of feeding type and probiotic potential. Three separate trials were conducted to compare the effects of Total Mixed Ration (TMR) cow feeds enriched with polyunsaturated fatty acids against control feeds. Milk samples, collected from the feeding trials, were fermented with three Lactobacillus strains categorized based on their probiotic potential: moderate (M), non-probiotic (N), and probiotic (P). The probiotic (P) strain exhibited distinct biochemical changes that were easily identifiable by both technologies. The NIRS and E-nose datasets were analysed separately to highlight the individual strengths and unique contributions of each technique in discriminating sample attributes. Specific NIRS wavelengths (1600–1800 nm), associated with unsaturated fatty acids like oleic and linoleic acids, acted as reliable markers for distinguishing milk samples based on the feeding type, while the 1300–1600 nm range helped differentiate strains. E-nose analysis identified volatile compounds such as hexanal and 1-hexen-3-one, formed from the oxidative degradation of unsaturated fatty acids, highlighting the impact of bacterial strains and milk composition on aroma and flavor. The fatty acid profile, particularly the unsaturated fatty acids and their derivatives, played a crucial role in strain and diet selection, offering valuable insights into the development of fermented milk products with specific probiotic characteristics.

Access the full paper free of charge on the website of the journal:
» Uncovering key factors in differentiating fermented milk by feeding type and probiotic potential with E-nose and NIRS techniques
Instrumental Aroma Analysis
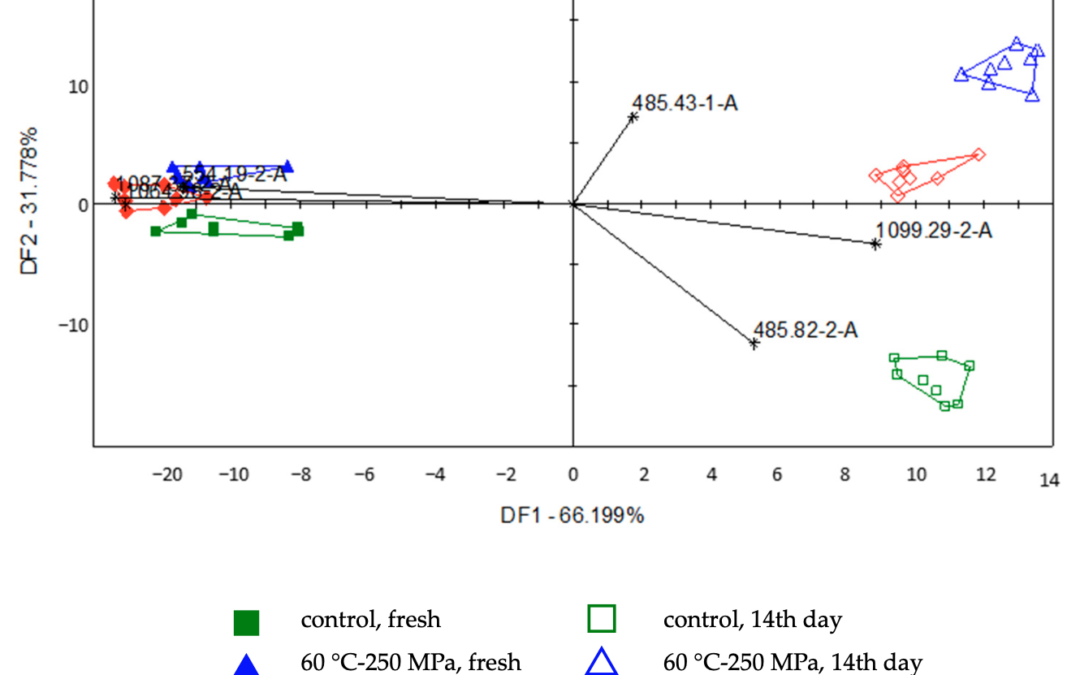
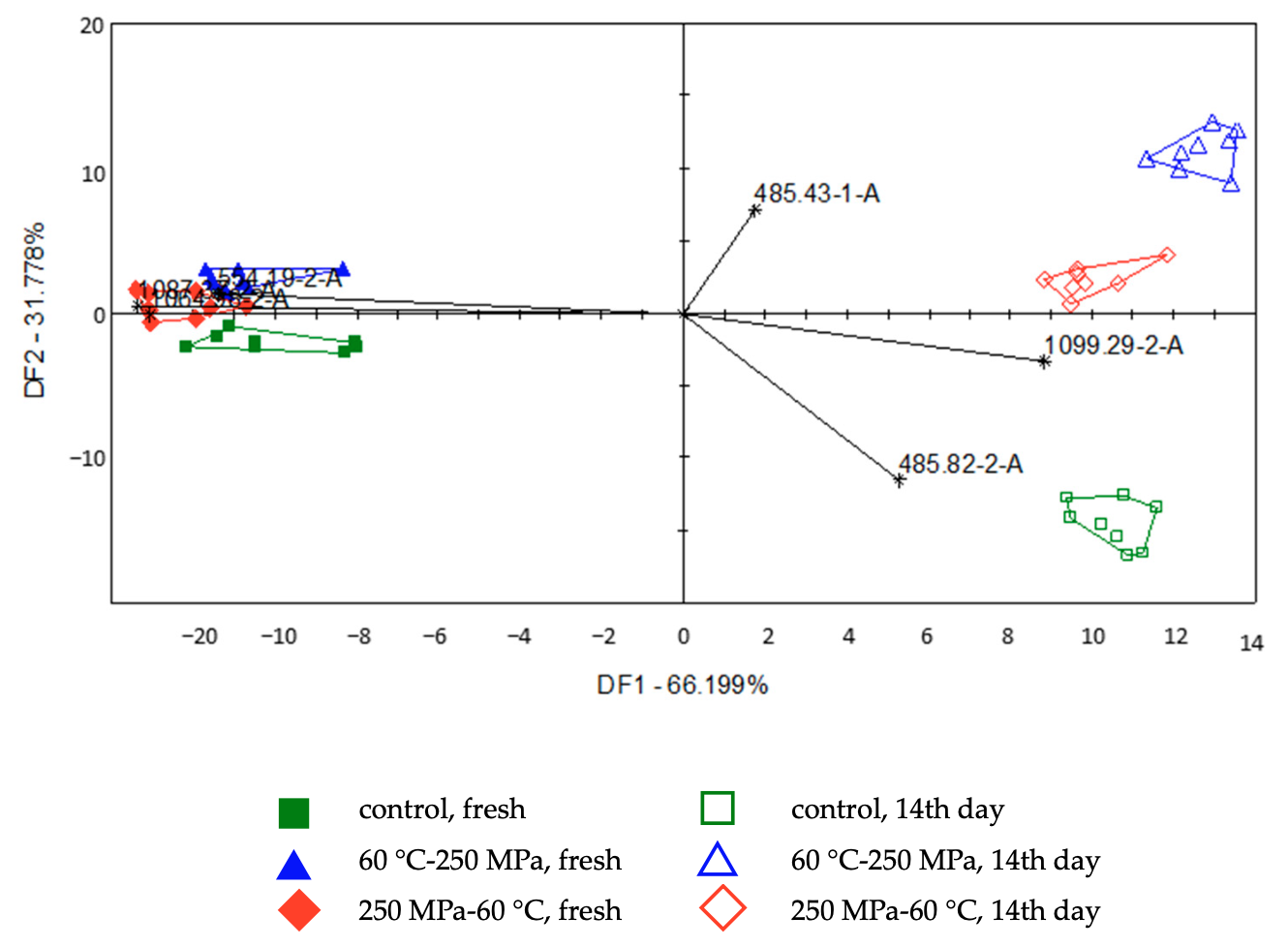
The preservation method can significantly affect the shelf life of foods, as well as the sensory properties, and the dynamics of their changes during storage. During the research conducted with colleagues from MATE, Hungarian University of Agriculture and Life Sciences, we examined smoothies preserved with heat treatment and high hydrostatic pressure using rapid instrumental analytical methods, which results were compared with the results of microbiological, physical and sensory tests. The article was published in the open-access journal Applied Sciences.
Shelf Life and Organoleptic Attributes of Multifruit Smoothies Treated by Combined Mild Preservation Technologies
Fanni Zakariás, Karina Ilona Hidas, Zoltan Kovacs, György Bázár, Andrea Taczman-Brückner, István Dalmadi, Gabriella Kiskó
The application of high hydrostatic pressure and mild heat treatment represents preservation processes for extending the shelf life of food products without compromising their quality. The combination of these physical methods at lower applied levels represents a promising approach to preserving the quality of treated products. This study aims to investigate the impact of combined treatments on the quality and storage stability of strawberry, banana, almond milk and avocado smoothies. The total colony count, electronic nose and tongue signals, colour, viscosity and sensory properties were examined over a 14-day storage period at 6 °C. The combined treatments were found to be effective in reducing the total colony count. During the sensory analysis, the impact of storage was the most prominent factor. Both the treatments and storage conditions significantly affected the colour characteristics of the samples. The smoothie samples exhibited pseudoplastic flow behaviour. Both applied treatments resulted in enhanced texture stability of the samples during the storage period. The electronic tongue and nose could differentiate between groups of fresh and stored samples, as well as between control and treated samples.
Access the full paper free of charge on the website of the journal:
» Shelf Life and Organoleptic Attributes of Multifruit Smoothies Treated by Combined Mild Preservation Technologies

News
It is often difficult to compare two or more devices, either during development or purchase, especially when they are operating in different parts of the world during testing. Based on the examination of coffee capsules of consistent quality, which are easily available worldwide, we have developed a methodology with which instrumental aroma testing technologies operating on different principles can be quickly compared, regardless of whether they operate in the world. Our article published in the journal Chemosensors presents the results of three significantly different devices. The surprisingly similar results show a good correlation with the results of human sensory properties. The method is suitable for comparing newly developed technologies with previous, already proven technologies; assessing their reliability, and determining which technologies provide results that are more closely related to human sensory properties; and which technologies reinforce or complement each other depending on whether they provide identical or different results when examining the same set of samples.
Read more


News
A new book titled “Sustainable Animal Agriculture – Global Challenges and Practical Solutions” is being published by the London-based publisher IntechOpen. In response to the honorable request, our colleagues contributed to the book by preparing a chapter on green agricultural technologies and sustainable analytical methods, presenting the latest trends. The book chapter, published in the summer of 2025, can be downloaded for free from the publisher’s website.
Read more

News
ADEXGO Kft. participated in the development of an in-farm forage testing device based on a new measurement methodology in the GINOP+ project of Geo-Milk Kft. and Neumann János University. The aim of the three-year project was to significantly improve the precision and accuracy of near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) testing of forages with high water content, heterogeneous appearance and extremely diverse composition under farm conditions using a novel sample preparation technology. The developed measuring device allows us to perform more reliable on-site rapid testing. Thanks to this, feeding specialists can make decisions based on objective data that improve the quality of feeding, increase production efficiency and reduce environmental impact.

Events
The BIOSYS – Biosystems and Food Engineering International Conference was held for the sixth time in June 2025. Our colleagues are regular participants in the conference series organized in Budapest by MATE, Hungarian University of Agriculture and Life Sciences. This time we participated with a study presenting the aroma analysis of animal products from feeding trials.

















